Medical instruments are specialized devices designed for diagnostic, therapeutic, and surgical procedures. They are made from high-quality materials that ensure sterility, precision, and safety when used with patients.
Our products
Medical gas central stations
Oxygen gas manifold
The oxygen gas manifold is a system for storing, supplying, and controlling oxygen to hospital wards, operating rooms, and intensive care units. It provides a safe, stable, and continuous supply of oxygen for patients requiring therapeutic or respiratory support.
Compressed air manifold
The compressed air manifold is a system for the production, storage, and controlled supply of medical compressed air to various hospital departments and equipment. It ensures reliable, clean, and safe delivery of air for respiratory support, anesthesia, and operation of medical devices.

Nitrous oxide manifold
The nitrous oxide (N₂O) manifold is a system for the storage, supply, and control of nitrous oxide in medical facilities. It provides safe and precise dosing of the gas for anesthesia and pain relief, integrated with hospital panels and equipment.

Vacuum manifold
The vacuum manifold is a system for generating, storing, and controlled delivery of vacuum in medical facilities. It provides reliable negative pressure for aspiration procedures, operation of surgical and intensive care devices, and ensures the safety of medical staff.

Carbon dioxide manifold
The carbon dioxide (CO₂) manifold is a system for storage, supply, and controlled dosing of CO₂ for medical applications, most commonly in surgery (e.g., laparoscopic procedures) and specialized therapies. It provides safe, precise, and stable delivery of the gas to equipment and patients.

Nitrogen manifold
The nitrogen manifold is a system for storage, supply, and controlled dosing of nitrogen (N₂), used in hospital practice and laboratory applications. It provides safe, precise, and continuous delivery of nitrogen to various medical devices and systems, maintaining high standards of safety and quality.
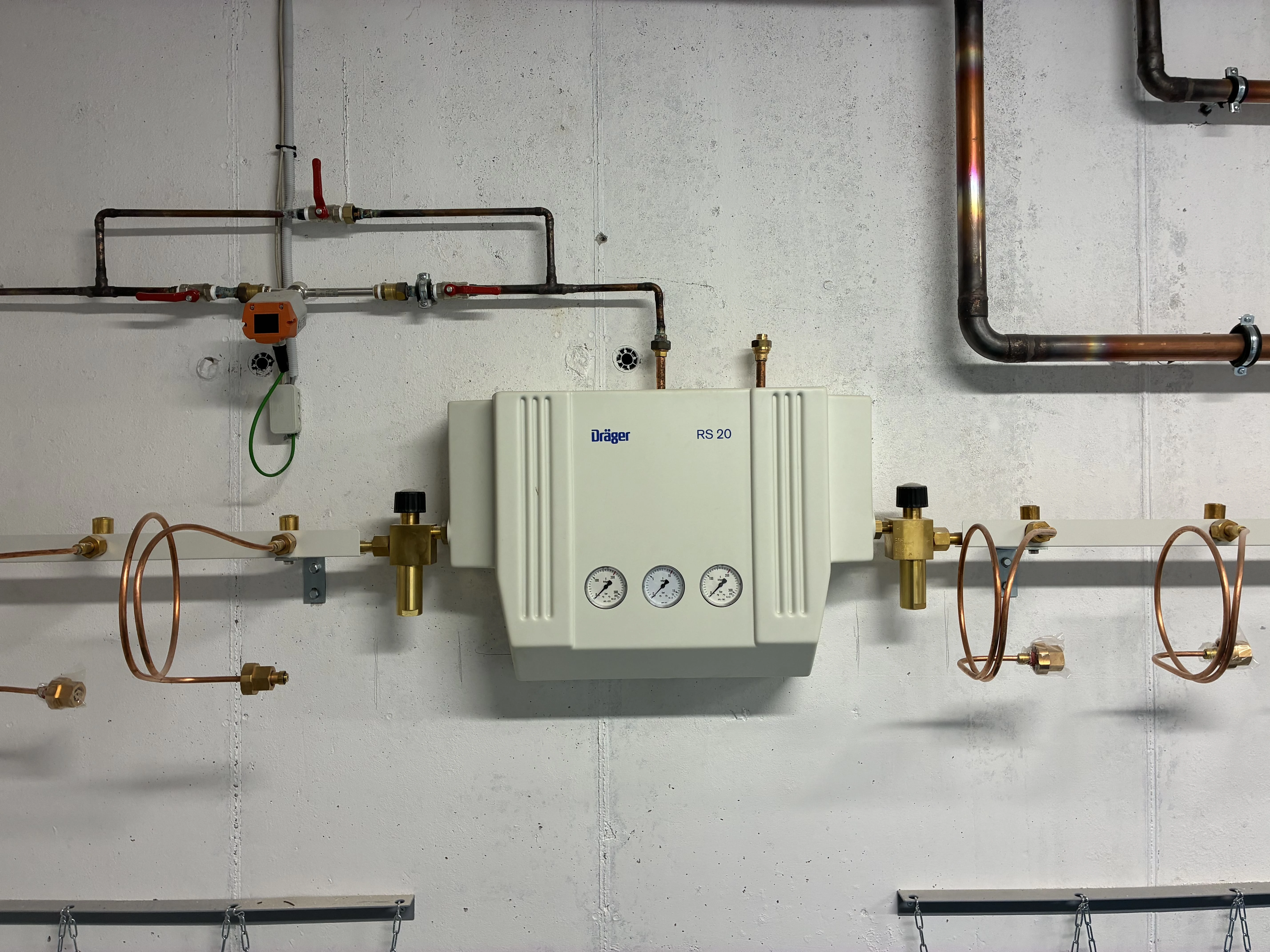

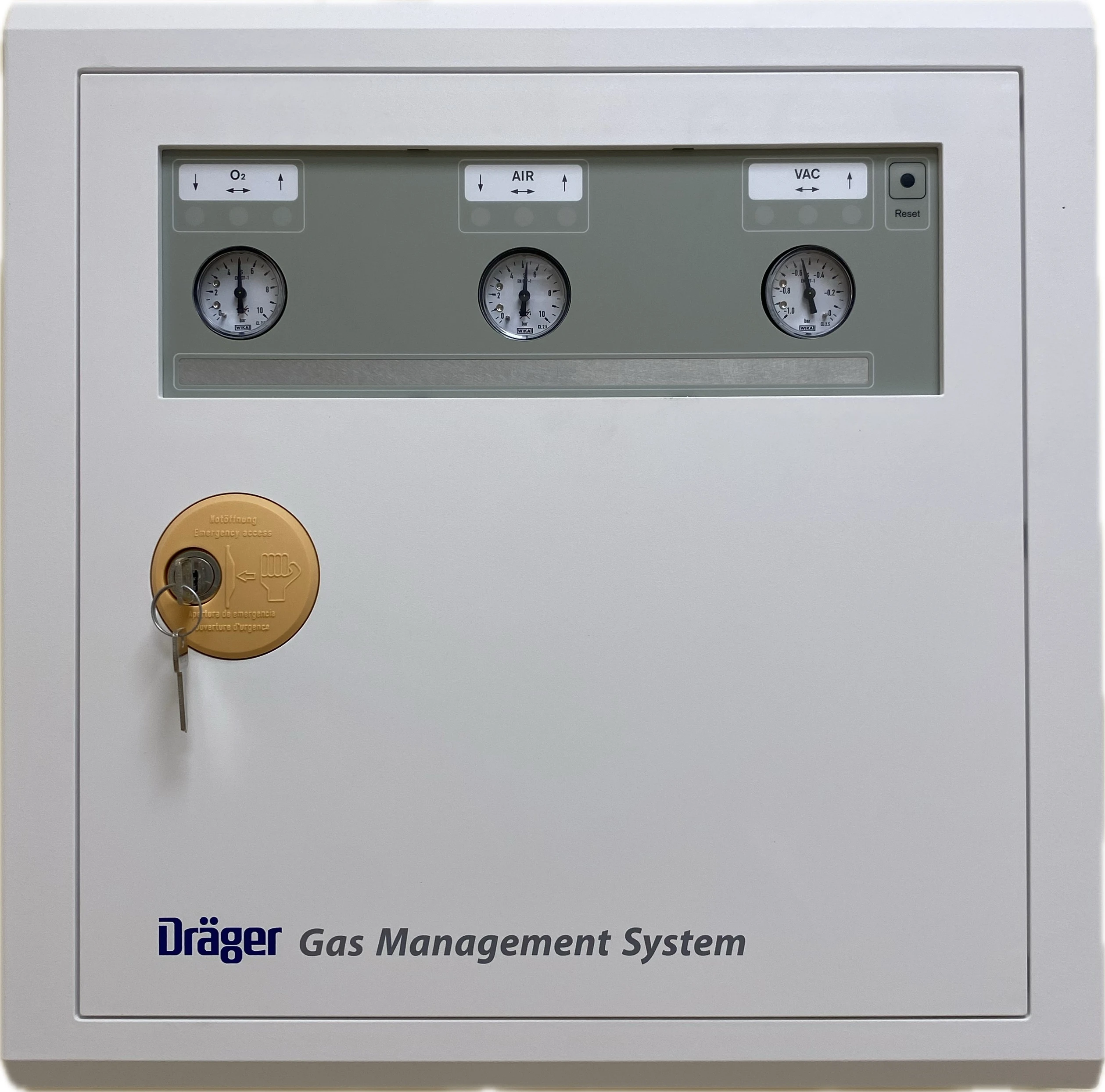
Control-closing boxes
Control-closing boxes
Control-closing boxes are key components of a centralized gas supply system in hospitals. They provide safe, organized, and controlled distribution of medical gases (oxygen, vacuum, air, nitrous oxide, and CO₂) from the main source to individual hospital panels or workstations on each floor.

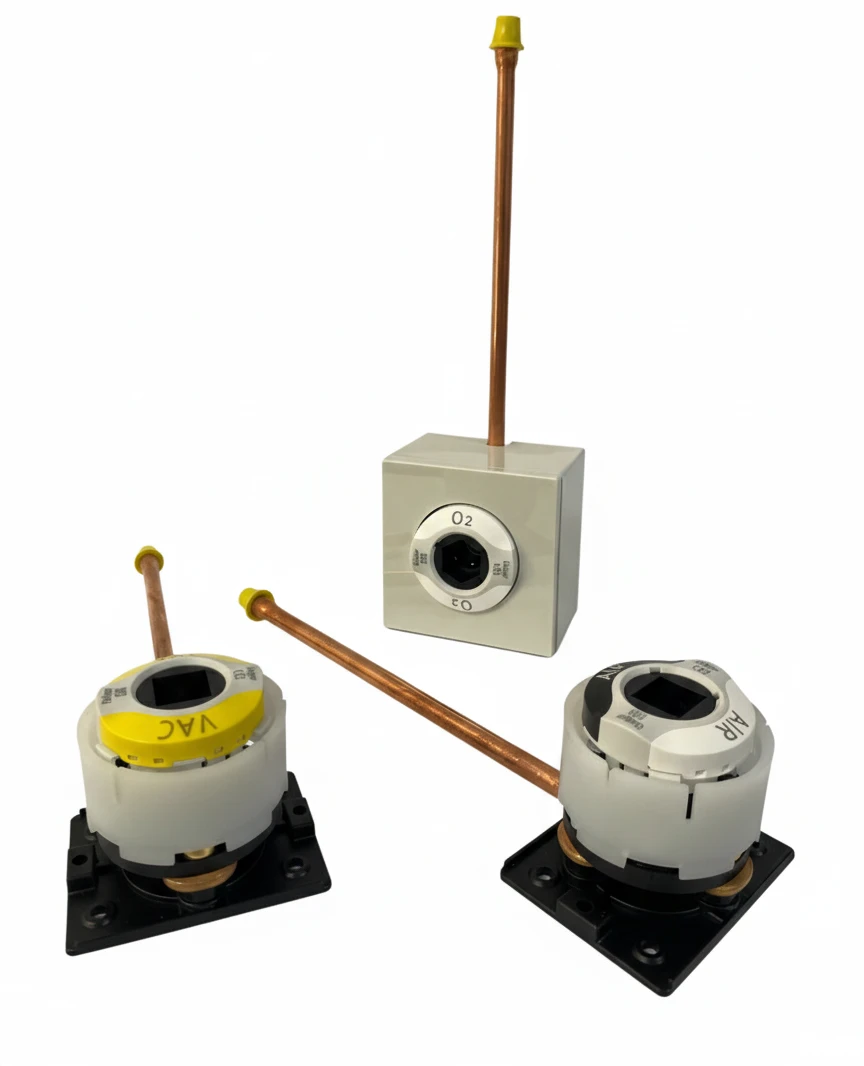
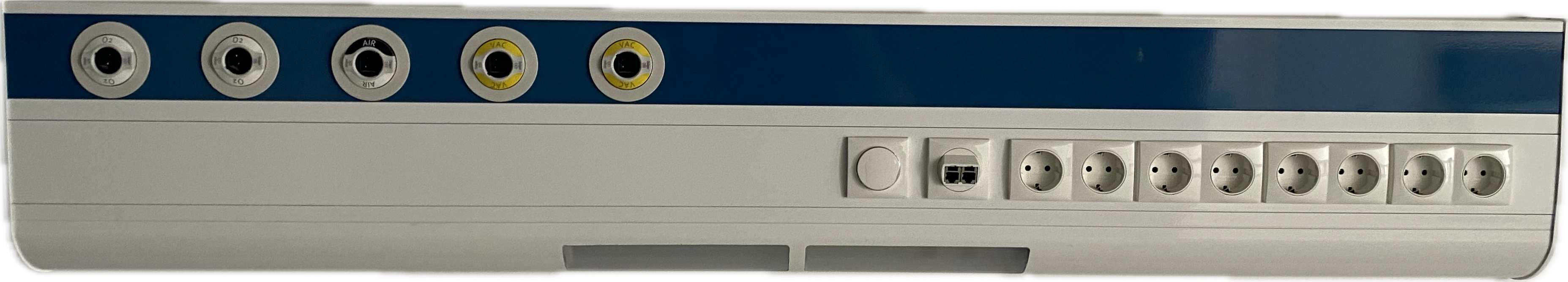
Outlets (medical gas outlets)
Terminal units
Hospital terminal units are specialized devices designed for the controlled delivery of medical gases and vacuum to patients and medical equipment. They provide accurate and safe dosing of gas or vacuum required for various therapeutic, anesthetic, or diagnostic procedures. The delivered gases include:
-
Oxygen (O₂) – for respiratory therapy, resuscitation, and oxygen therapy.
-
Vacuum – for aspiration and removal of bodily fluids during surgical and intensive care procedures.
-
Compressed air – for operation of medical devices, ventilators, and anesthesia.
-
Nitrous oxide (N₂O) – primarily used as an anesthetic and analgesic agent.
-
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) – for laparoscopic procedures or specific therapeutic applications.

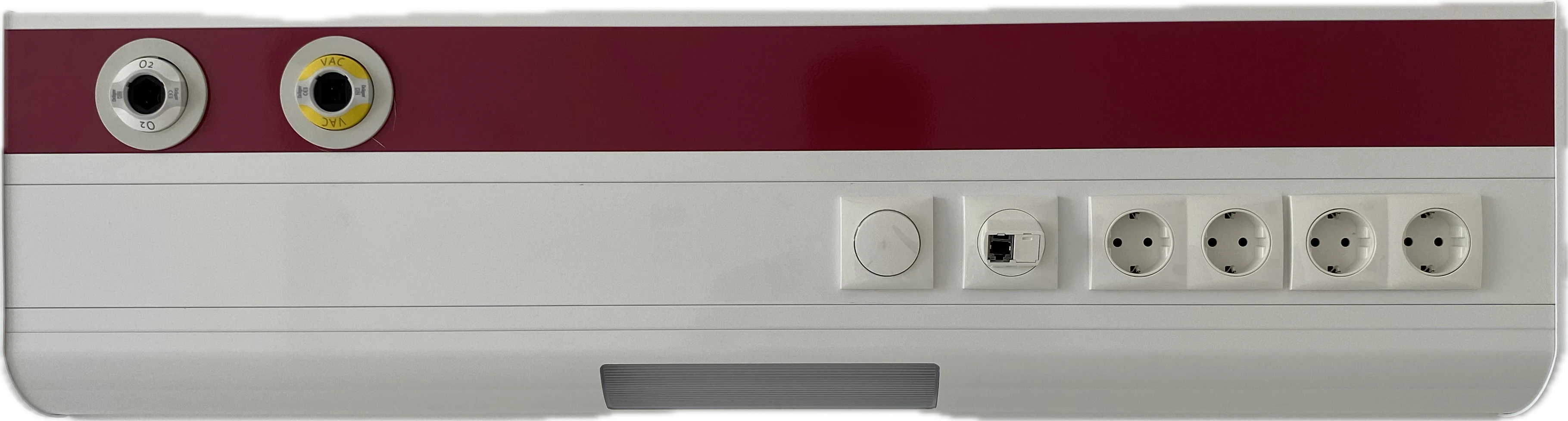
Hospital Bed Head Units
Hospital Bed Head Units
Wall-mounted hospital BHU are the most common solution for delivering medical gases, electrical power, communication, and lighting directly to the hospital bed. They are installed horizontally or vertically on the wall of the hospital room and provide a safe, organized, and convenient environment for both patients and medical staff.

Hospital wall-mounted intensive care Bed Head Units
Wall-mounted hospital intensive care BHU are designed for intensive care units, resuscitation rooms, and emergency departments where patients are under constant monitoring and require multiple medical connections and equipment. These wall-mounted intensive care panels are high-functionality systems installed directly on the wall in resuscitation rooms and intensive care units.

Hospital ceiling-mounted intensive care Bed Head Units
Hospital ceiling-mounted BHU are specialized medical systems installed on the ceilings of hospital rooms, intensive care units, or operating theaters. They provide centralized delivery of medical gases, electrical power, communications, and convenient mounting for medical equipment, while freeing up space around the patient and improving the ergonomics of the working environment.

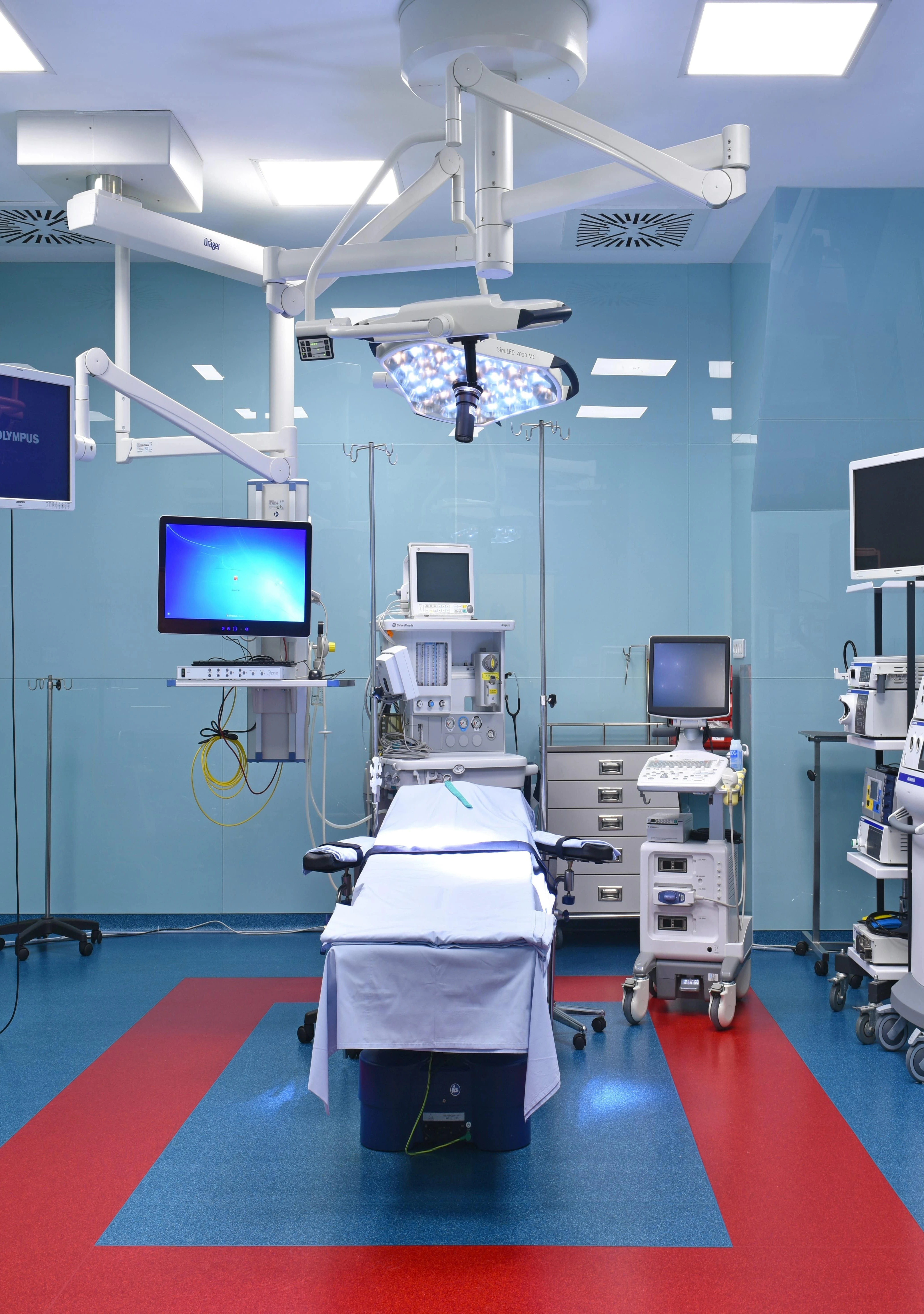
Ceiling-mounted columns
Ceiling-mounted columns
The operating column is a high-tech device used in operating rooms and intensive care units. It provides safe and ergonomic access to medical gases, electrical power, communication systems, and equipment, while optimizing the workspace.
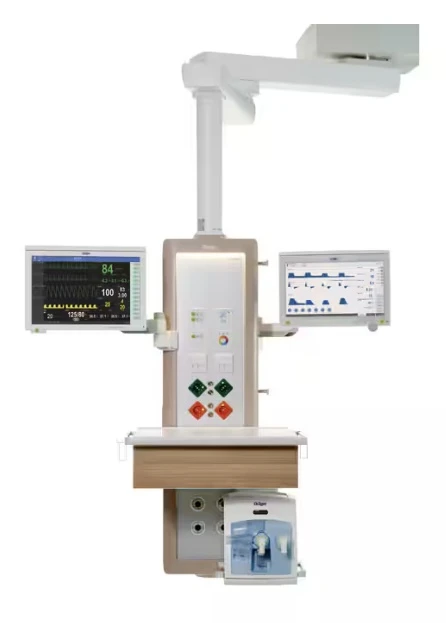
Ceiling-mounted surgical lights
Ceiling-mounted surgical lights
Operating lights are a key element of the equipment in every operating room. They provide optimal illumination of the surgical field, free of shadows and without altering tissue colors, which is crucial for the safety and precision of surgical procedures. They can be equipped with an arm for a monitor and camera.

Mobil surgical lights
The mobile surgical light is a specialized medical lighting device designed to provide strong, uniform, and shadow-free illumination during surgical and diagnostic procedures. It is mounted on a mobile wheeled stand, allowing easy positioning and use in various settings — from operating rooms to treatment and examination rooms.

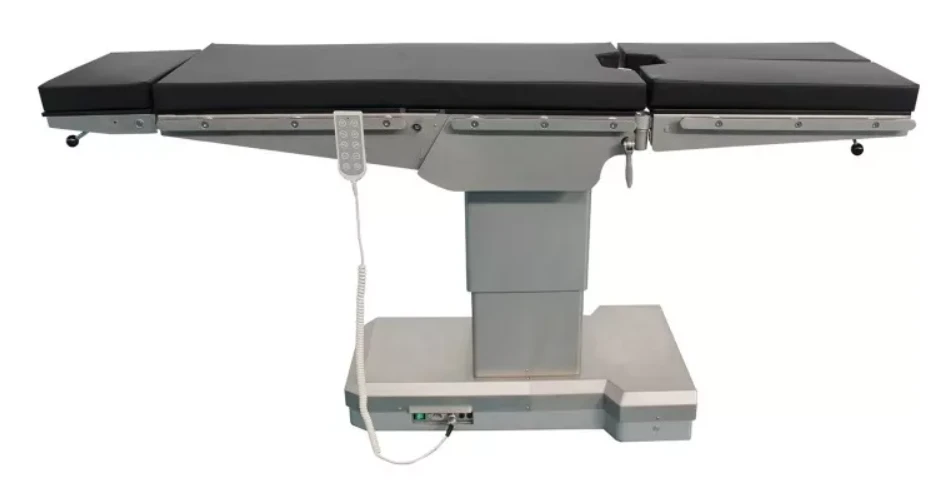
Operating tables
Operating tables
The operating table is essential equipment in every operating room. It serves to position and support the patient during surgical procedures and is characterized by high stability, ergonomics, and adaptability according to the type of surgery. There are several types:
-
Universal operating tables – suitable for a wide range of surgical interventions.
-
Specialized tables – for orthopedics, neurosurgery, urology, cardiovascular surgeries, and more.
-
Mobile tables – lightweight and easily movable, often used in smaller hospitals or emergency cases.
-
Hybrid tables – integrated with X-ray and imaging systems, suitable for highly specialized interventions.

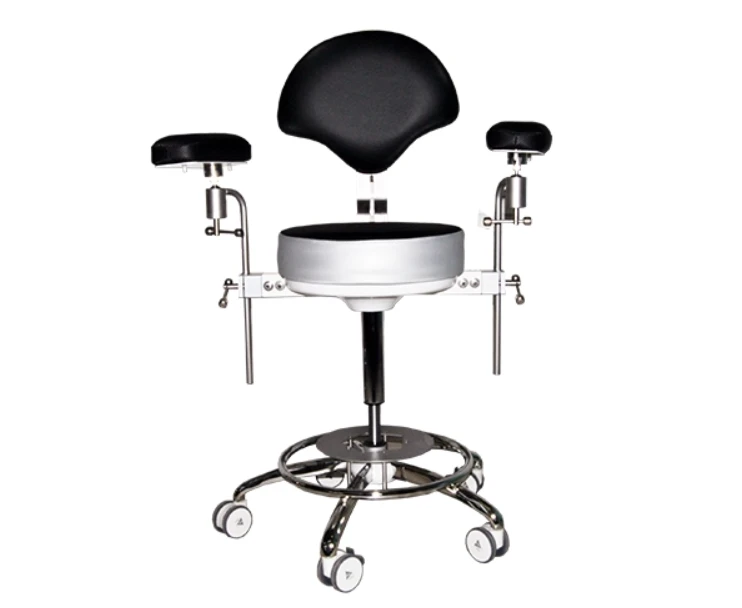
Operating chair
The surgical chair is an ergonomically designed seat intended to provide comfort, stability, and an optimal working position for the medical professional during prolonged surgical procedures. This type of chair supports proper posture, reduces physical strain, and enhances the precision of movements during work.

Instruments for IMG
Supportive rails
The rails above hospital panels are metal (stainless steel) bars installed above beds or workstations in hospitals. They are used for the organized mounting and movement of medical equipment, such as monitors, infusion pumps, suction devices, and other life-support equipment.

Monitor stands
Monitor mounts are specialized devices designed for stable attachment and positioning of medical monitors in hospital rooms, operating theaters, and intensive care units. They provide ergonomic access to the displays, ensuring the safety of both staff and patients.

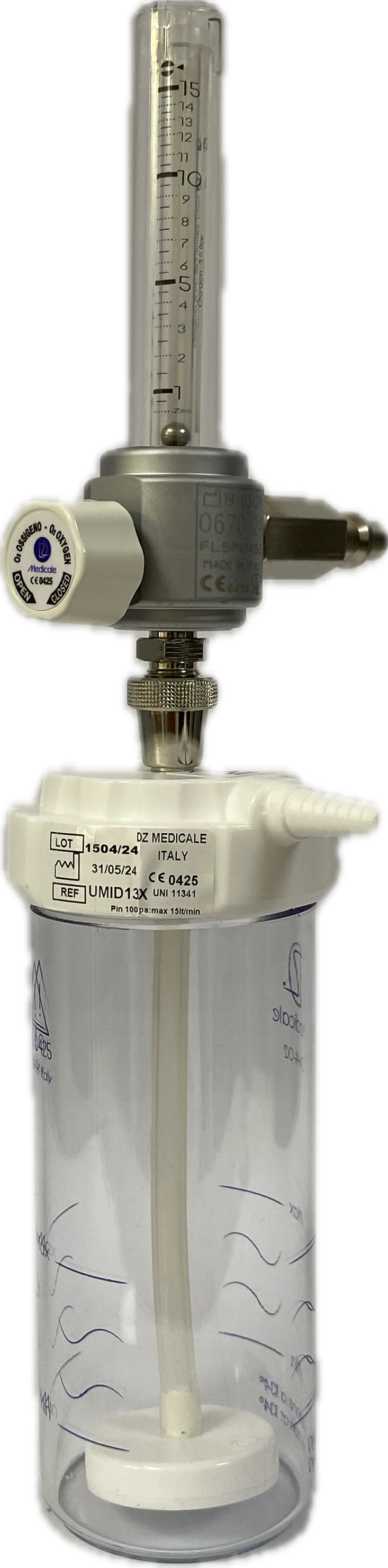
Flowmeter
The flowmeter is a measuring instrument used for precise dosing and control of gas flow in medical and laboratory settings. In hospital practice, it is primarily used to regulate oxygen, air, and other medical gases supplied to patients through panels, devices, or ventilators.

Vacuum regulator
The vacuum regulator (for thoracic and bronchial aspiration) is a device designed for controlled creation and maintenance of negative pressure (vacuum) in medical aspiration systems. It ensures safe and precise operation of aspiration pumps, allowing effective suction of bodily fluids, secretions, or other substances during surgical and intensive care procedures.
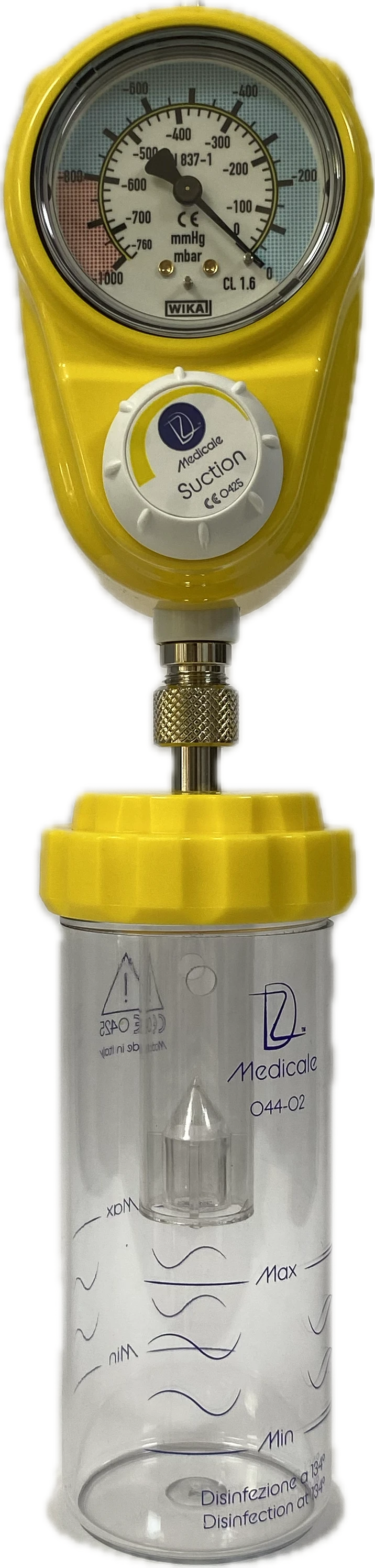

Suction container
The suction container (1, 2, or 4 liters) is a medical vessel designed for collecting and temporarily storing bodily fluids during surgical, intensive care, and therapeutic procedures. It is usually used in combination with aspiration systems and vacuum regulators, ensuring safe and hygienic operation for medical staff.
Medical equipment
Devices
Medical devices are electronic or mechanical instruments designed for diagnosis, monitoring, therapy, and support of the patient’s vital functions. They are essential for the effective operation of intensive care units, operating rooms, and emergency departments.
- Anesthesia machines
- Infusion pumps
- Syringe pumps (perfusion pumps)
- Surgical suction devices
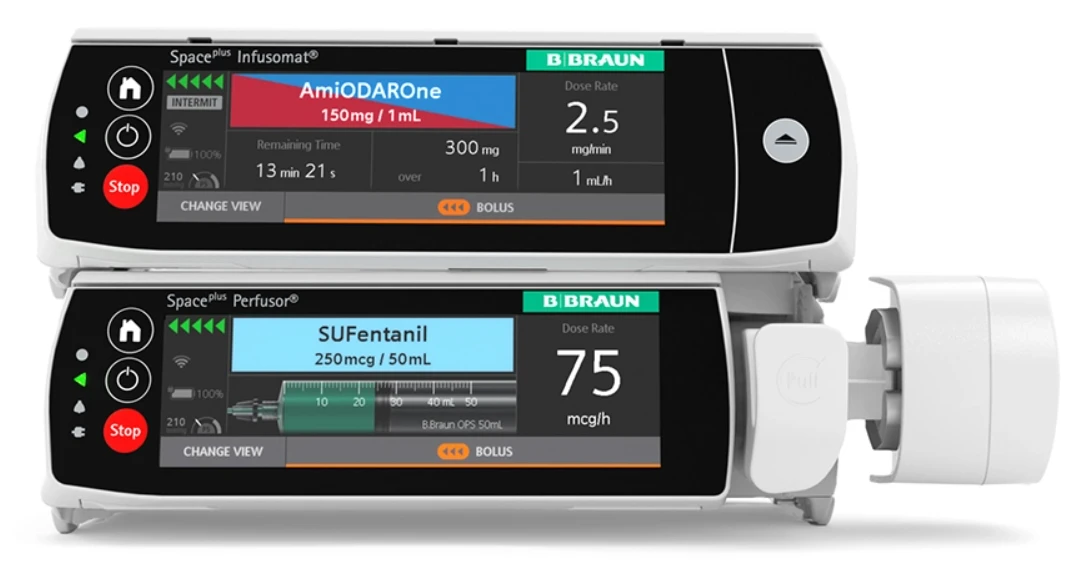

Instruments
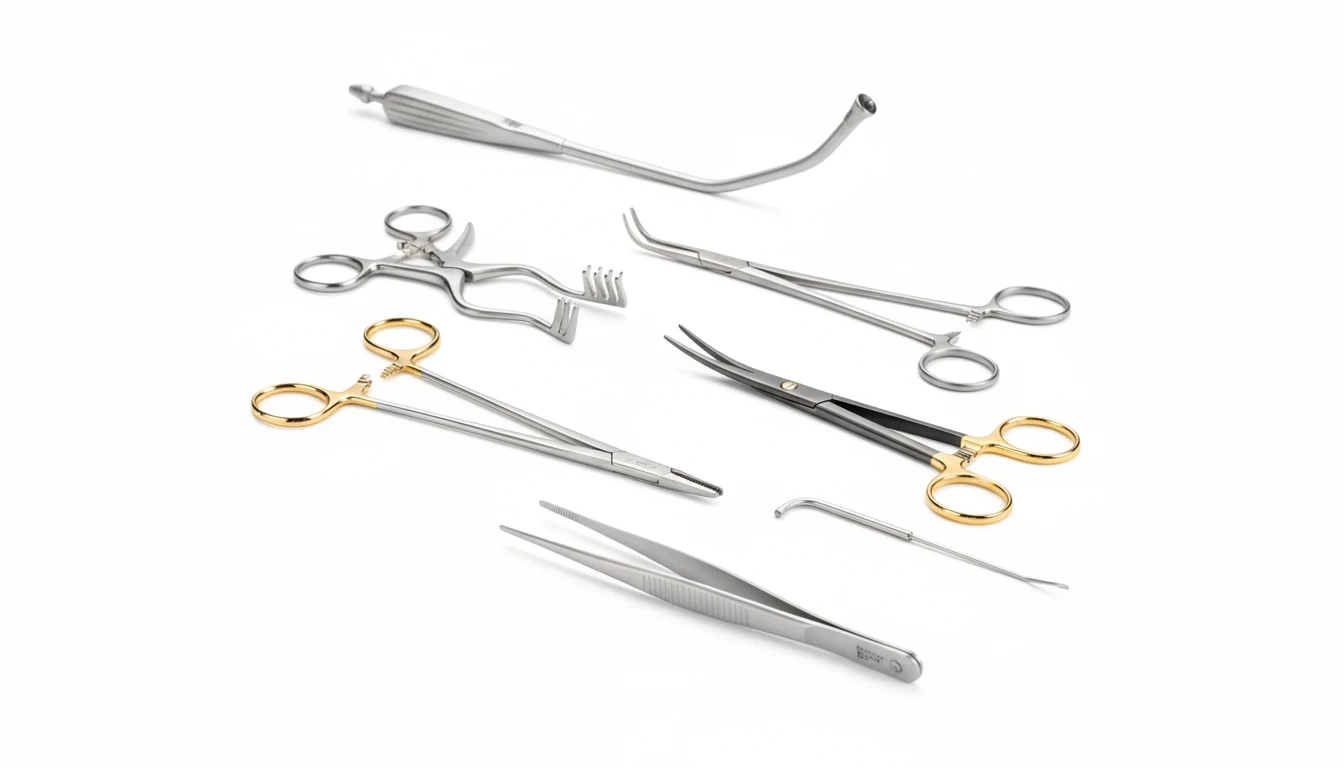
Sterilization containers
Sterilization containers are reusable, durable, and airtight systems for packaging, transporting, and storing surgical instruments, intended for use in hospitals, operating rooms, sterilization departments, and clinics. They ensure the safe and reliable handling of instruments throughout the entire sterilization cycle — from preparation, through the sterilization process, to storage and delivery to the operating room.

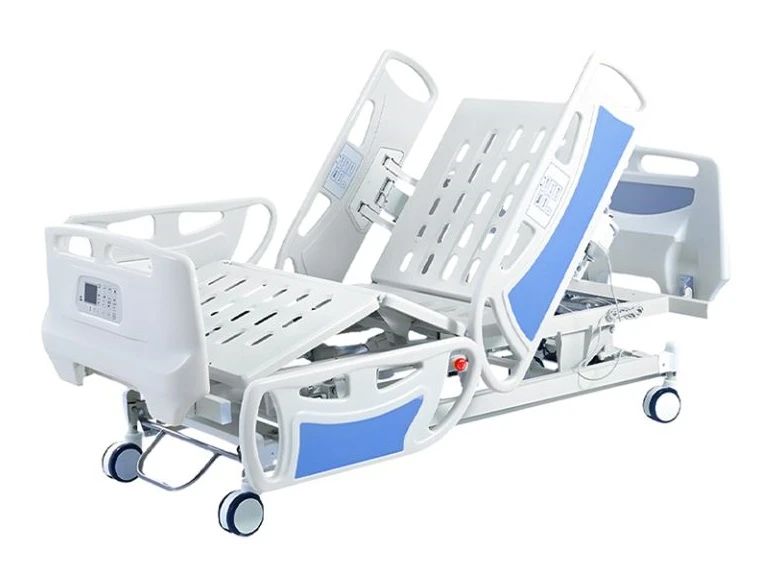
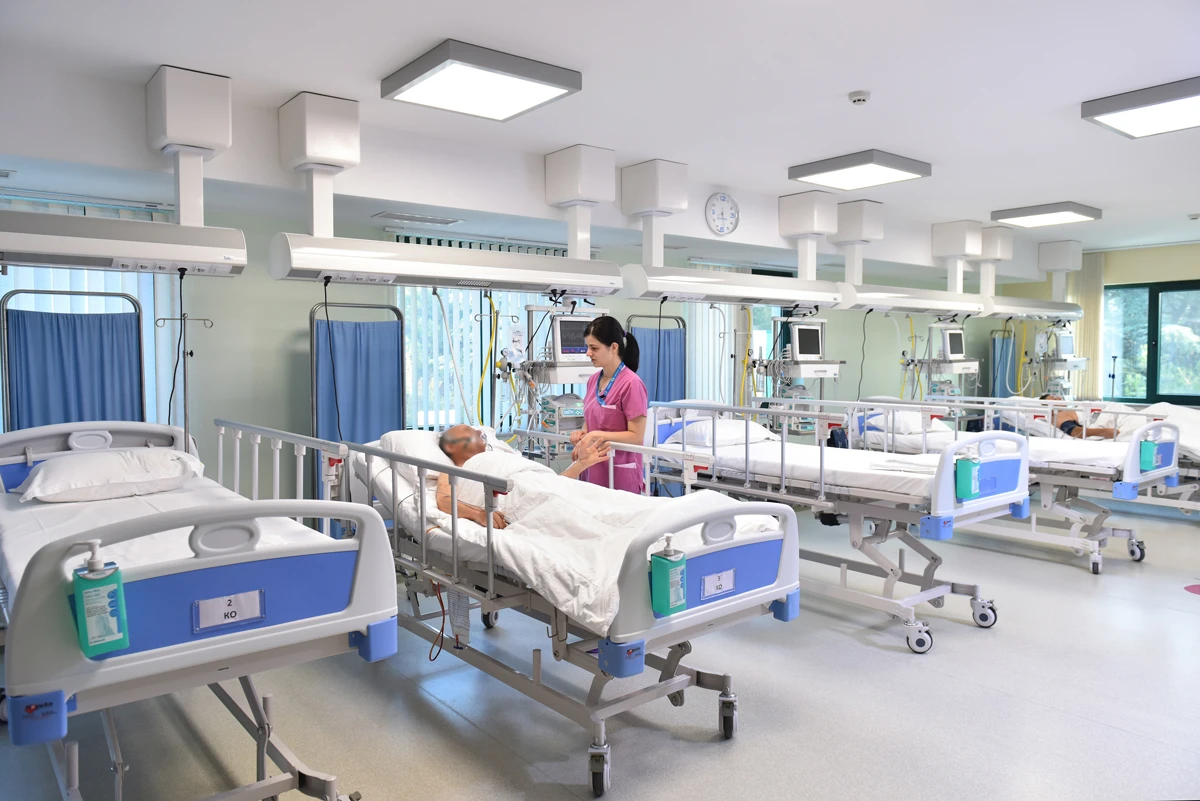
Hospital beds
A hospital bed is specialized medical equipment designed to provide comfort, safety, and optimal patient positioning during treatment and recovery. It features adjustable head, body, and leg sections that can be controlled mechanically or electrically, supporting both the patient and the medical staff. Integrated safety rails, a robust construction, and lockable wheels ensure security and mobility, while the option to add accessories allows the bed to be tailored to various medical needs.
Hospital care
Hospital consumables for single-use or short-term use, which are necessary for the diagnosis, treatment, and hygiene of the patient. They are divided into several main categories:
- Infusion therapy
- Intravenous access
- Wound care
- Disinfectants
- Protective equipment
Cabinets and furniture
Hospital cabinets and medical furniture are specialized items designed to provide safe, hygienic, and efficient organization of the workspace in healthcare facilities. They are used for storing medications, consumables, instruments, documentation, and patients’ personal belongings, as well as for equipping treatment rooms, operating rooms, wards, and laboratories.





